2023 1Q W03 주간업무 (서종원)
PDCA
| 전공교육 | 개발실습 | 부서교육 | 부서업무지원 | 기타 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | 과학데이터교육 일 3.2시간 이상 수강 | p4 tutorial실습 | 우수성과취합 마무리 | ||
| D | 텍스트 데이터분석 수강, 인공지능 부분 수강 | basic forwarding 실습, basic tunnel 실습,P4runtime실습, mri 실습,소스라우트 실습, 부하분산 실습 | 우수성과 취합 마무리 및 검토 | ||
| C | 텍스트 데이터분석 수강, 인공지능 부분 수강 | basic forwarding 실습, basic tunnel 실습,P4runtime실습, mri 실습,소스라우트 실습, 부하분산 실습 및 이해, 단순한 계산기 구현 | 우수성과 취합 마무리 및 검토 | ||
| A |
일일회고
23/02/13
- Fact : P4 실습환경을 구축하고 기본적인 forwarding 을 실습해보았다, 우수성과취합을 진행했다.
- Feelings : 새로운 언어를 배우는 것은 언제나 어렵지만 c언어와 비슷한 면이 있어서 다행이다.
- Finding : 네트워크를 효율적으로 관리하는 프로그래밍 언어가 있다는 것을 처음 알았다.
- Future Action Plan : 우수성과 취합, P4 튜토리얼을 보면서 다음 내용 실습
- Feedbacks :
23/02/14
- Fact : P4 basic forwarding의 관련 문서들을 보고 작동 방식을 이해했다. 우수성과취합을 완료했다.
- Feelings : 패킷을 직접 건들여보니 이해가 더욱 잘되는 느낌이었다.
- Finding : basic forwarding의 작동 방식을 이해했다.
- Future Action Plan : 우수성과 취합 검토, P4 튜토리얼을 보면서 다음 내용 실습
- Feedbacks :
23/02/15
- Fact : 우수성과취합 검토까지 완료, P4 basic tunnel의 관련 문서들을 보고 작동 방식을 이해했다.
- Feelings : 뭔가 배워가고 있다는 느낌이 든다.
- Finding : 터널링에 대한 것을 처음 알았다.
- Future Action Plan : P4 runtime 이해
- Feedbacks :
23/02/16
- Fact : P4 튜토리얼의 P4runtime과 mri를 실습해보고 이해하였다.
- Feelings : 생각보다 경로를 추척하기 위한 mri의 구조가 단순해서 놀랐다.
- Finding : 첫날에 들었던 INT의 축소된 버전을 해보면서 어떤식으로 경로를 모니터링 할 수 있는지 알았다.
- Future Action Plan : P4 소스포워딩
- Feedbacks :
23/02/17
- Fact : P4 튜토리얼의 P4sourceroute와 P4 loadbalancing을 실습해보고 이해하였다.
- Feelings : 어느정도 기본적인 P4 코드를 짤 수 있을 것 같다.
- Finding : 새로운 소스라우트와 로드밸런싱을 배웠다.
- Future Action Plan : P4의 남은 튜토리얼 수행
- Feedbacks :
Memo
23/02/13
- 참고사항
- P4 튜토리얼 https://github.com/p4lang/tutorials
- P4 실습환경 구축
- P4 basic forwarding 튜토리얼 실습 https://github.com/p4lang/tutorials/tree/master/exercises/basic
- P4 언어 공식 문서 https://p4.org/specs/
- 동영상 참고
출처 | 왜 | 내용 | 배운 점 및 기억해야할 점 | 비고 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 과학데이터교육 텍스트데이터분석 | 충북대 현장실습 직무교육 | 텍스트 마이밍 기법, 텍스트 문장의 형태소 분석, 필요 단어 추출 텍스트 처리 방법 | 3차시까지 수강 |
23/02/14
- 참고사항
- 패킷의 이해 https://blog.naver.com/sujunghan726/220315439853 → Ethernet 패킷과 IPv4패킷의 이해
bmv2 소프트웨어 스위치에 구현된 V1Model 아키텍처 https://github.com/p4lang/p4c/blob/main/p4include/v1model.p4 → 독립형 또는 Mininet에서 P4 소프트웨어 스위치를 실행하기 위한 시뮬레이션 환경인 mv2에 구현된 소프트웨어 스위치
- 동영상 참고
출처 | 왜 | 내용 | 배운 점 및 기억해야할 점 | 비고 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 과학데이터교육 텍스트데이터분석 | 충북대 현장실습 직무교육 | 문장 의미 분석, 단어 빈도 및 연관성 수치 계산, 텍스트 데이터 분석 프로세스 기획, 텍스트 데이터 분석 기법 | 7차시까지 수강 |
23/02/15
- 참고사항
-
- 동영상 참고
출처 | 왜 | 내용 | 배운 점 및 기억해야할 점 | 비고 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 과학데이터교육 텍스트데이터분석 | 충북대 현장실습 직무교육 | 텍스트 데이터 분석 모델 평가 및 구현하기, 토픽별 필요 단어 분류, 긍정 및 부정 감성분석 사전 제작, 데이터 예측을 위한 머신러닝 기법 | 11차시까지 수강 |
23/02/16
- 참고사항
-
- 동영상 참고
출처 | 왜 | 내용 | 배운 점 및 기억해야할 점 | 비고 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 과학데이터교육 텍스트데이터분석 | 충북대 현장실습 직무교육 | 데이터 시각화, 정형-비정형 데이터 분석 모델 기획, 공공 데이터 분석, 분석 목적 인사이트 도출, 예측 및 데이터 평가 | 텍스트데이터분석 수강 끝 |
23/02/17
- 참고사항
- 동영상 참고
출처 | 왜 | 내용 | 배운 점 및 기억해야할 점 | 비고 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 과학데이터교육 인공지능 | 충북대 현장실습 직무교육 | 인공지능의 소개, 인공지능의 발달사, 에이전트 정의 및 지능형 에이전트, 에이전트 환경과 에이전트 아키텍처 | 4차시까지 수강 |
배운 것 및 기억해야할 것
P4 튜토리얼 basic forwarding의 이해
튜토리얼 코드 리뷰
/* -*- P4_16 -*- */
#include <core.p4>
#include <v1model.p4>
const bit<16> TYPE_IPV4 = 0x800;
/*************************************************************************
*********************** H E A D E R S ***********************************
*************************************************************************/
typedef bit<9> egressSpec_t;
typedef bit<48> macAddr_t;
typedef bit<32> ip4Addr_t;
//ethernet의 기본 헤더
header ethernet_t {
macAddr_t dstAddr;
macAddr_t srcAddr;
bit<16> etherType;
}
//IPv4의 기본 헤더
header ipv4_t {
bit<4> version;
bit<4> ihl;
bit<8> diffserv;
bit<16> totalLen;
bit<16> identification;
bit<3> flags;
bit<13> fragOffset;
bit<8> ttl;
bit<8> protocol;
bit<16> hdrChecksum;
ip4Addr_t srcAddr;
ip4Addr_t dstAddr;
}
struct metadata {
/* empty */
}
struct headers {
ethernet_t ethernet;
ipv4_t ipv4;
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** P A R S E R ***********************************
*************************************************************************/
//패킷에서 헤더를 분리
//packet_in packet은 스위치에 들어오는 패킷
//out headers hdr은 패킷에서 분리된 헤더들이 각각 저장될 변수같은것
//start 상태로 시작해서 모든 헤더 분리가 정상적으로 끝난다면 accept 상태로 이동해서 정상종료, 아니라면 ignore 상태로 이동
parser MyParser(packet_in packet,
out headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
//패킷을 처음으로 전달받아서 시작된 상태
state start {
//parse_ethernet으로 상태 이동
transition parse_ethernet;
}
state parse_ethernet {
//패킷에서 ethernet헤더에 맞게 분리/추출
packet.extract(hdr.ethernet);
//패킷에서 분리된 ethernet 헤더에서 etherType 값이 위에서 정의된 TYPE_IPV4 0x800라면 parse_ipv4 상태로 이동, 0x800이 아닌 상태(default)라면 accept상태로 이동 -> 즉 c언어의 switch 같은 문법
transition select(hdr.ethernet.etherType) {
TYPE_IPV4: parse_ipv4;
default: accept;
}
}
state parse_ipv4 {
//패킷에서 추가적으로 ipv4 헤더 분리/추출
packet.extract(hdr.ipv4);
//패킷에서 추출 후에 accept 상태로 이동
transition accept;
}
}
/*************************************************************************
************ C H E C K S U M V E R I F I C A T I O N *************
*************************************************************************/
//체크섬 검증은 생략
control MyVerifyChecksum(inout headers hdr, inout metadata meta) {
apply { }
}
/*************************************************************************
************** I N G R E S S P R O C E S S I N G *******************
*************************************************************************/
//table을 참조하면서 패킷이 다음으로 이동할 경로 설정
control MyIngress(inout headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
//table에 match되는 ipv4의 dstAddr이 없다면 패킷을 삭제한다.
action drop() {
mark_to_drop(standard_metadata);
}
//table에 match되는 ipv4의 dstAddr이 있다면 실행되는 action으로 알맞은 dstAddr와 port를 인수로 전달받는다.
action ipv4_forward(macAddr_t dstAddr, egressSpec_t port) {
//해당 스위치/호스트에서 송신할때 쓰는 포트를 설정
//standard_metadata는 v1model 아키텍처에 의해 전달받은 구조체이며 패킷의 다양한 정보가 들어있다. 특히 standard_metadata.egress_spec는 패킷이 이동할 출력포트를 지정한다.
standard_metadata.egress_spec = port;
//이더넷의 헤더안의 srtAddr과 dstAddr을 알맞게 설정한다.
hdr.ethernet.srcAddr = hdr.ethernet.dstAddr;
hdr.ethernet.dstAddr = dstAddr;
//패킷이 이동할 때마다 ipv4의 ttl을 1씩 줄어들게한다.
hdr.ipv4.ttl = hdr.ipv4.ttl - 1;
}
//테이블을 정의한다.
table ipv4_lpm {
//테이블의 key와 match되는 방식을 설정한다.
key = {
hdr.ipv4.dstAddr: lpm;
}
//테이블의 모든 액션을 정의한다.
actions = {
ipv4_forward;
drop;
NoAction;
}
size = 1024;
//기본 액션을 정의한다.
default_action = drop();
}
//컨트롤 실행
apply {
//ipv4가 유효하다면 테이블 매칭을 실행한다.
if (hdr.ipv4.isValid()) {
ipv4_lpm.apply();
}
}
}
/*************************************************************************
**************** E G R E S S P R O C E S S I N G *******************
*************************************************************************/
control MyEgress(inout headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
apply { }
}
/*************************************************************************
************* C H E C K S U M C O M P U T A T I O N **************
*************************************************************************/
//ipv4 헤더의 내용이 변경되었으므로 체크섬 값도 그에 맞게 변경
control MyComputeChecksum(inout headers hdr, inout metadata meta) {
apply {
update_checksum(
hdr.ipv4.isValid(),
{ hdr.ipv4.version,
hdr.ipv4.ihl,
hdr.ipv4.diffserv,
hdr.ipv4.totalLen,
hdr.ipv4.identification,
hdr.ipv4.flags,
hdr.ipv4.fragOffset,
hdr.ipv4.ttl,
hdr.ipv4.protocol,
hdr.ipv4.srcAddr,
hdr.ipv4.dstAddr },
hdr.ipv4.hdrChecksum,
HashAlgorithm.csum16);
}
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** D E P A R S E R *******************************
*************************************************************************/
//새롭게 변경된 헤더들을 패킷으로 다시 묶음
control MyDeparser(packet_out packet, in headers hdr) {
apply {
packet.emit(hdr.ethernet);
packet.emit(hdr.ipv4);
}
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** S W I T C H *******************************
*************************************************************************/
//v1model의 기본적인 switch 아키텍처
V1Switch(
MyParser(),
MyVerifyChecksum(),
MyIngress(),
MyEgress(),
MyComputeChecksum(),
MyDeparser()
) main;
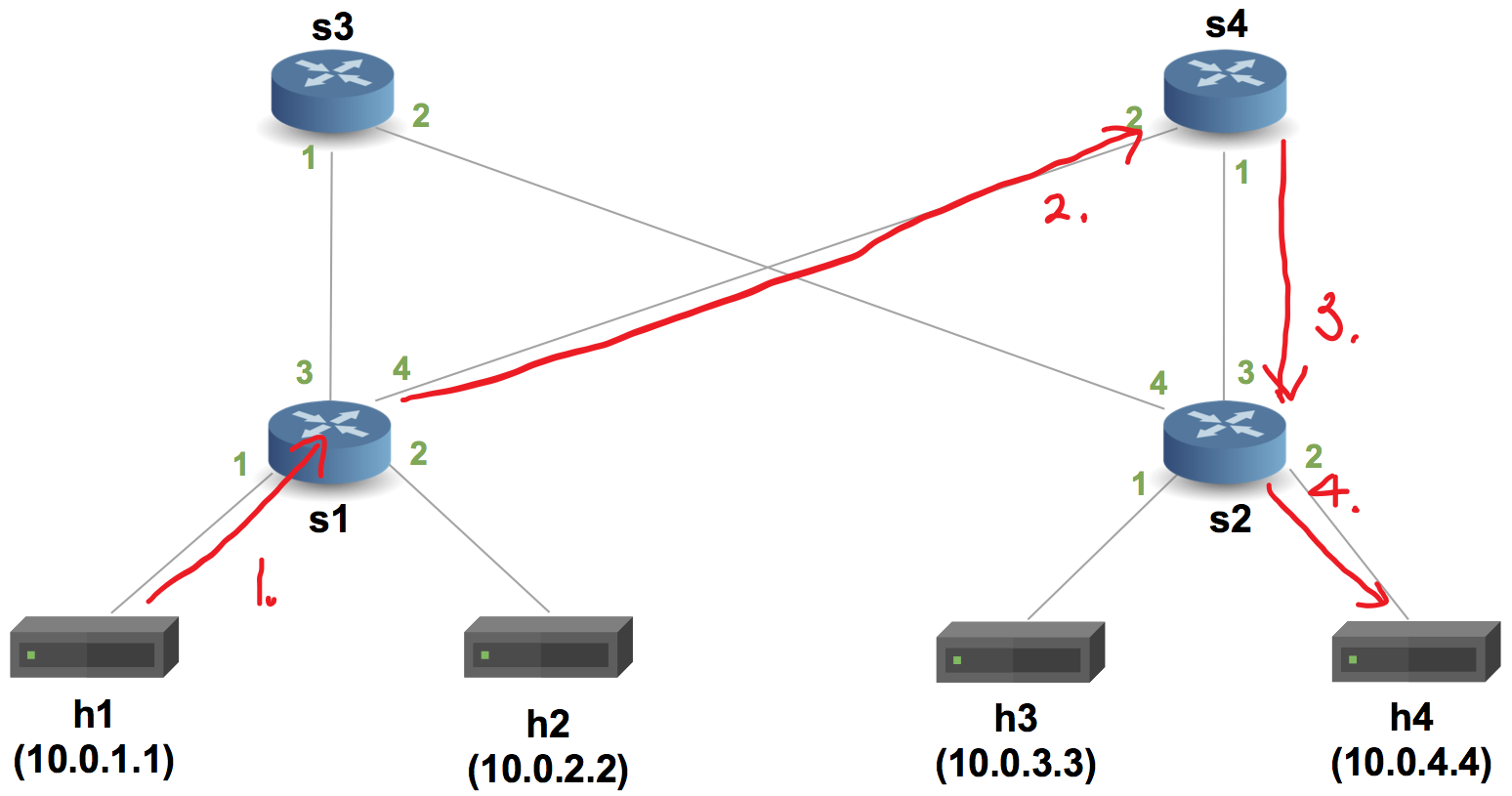
pod-topo 내의 sX-runtime.json 파일의 설정에 따른 패킷의 이동경로
https://github.com/p4lang/tutorials/tree/master/exercises/basic/pod-topo 의 sX-runtime.json은 스위치의 테이블 역할을 설정한다.
스위치의 테이블 내에 매치되는 목적지(ipAddr)의 다음 경로를 저장하고 있는다. 튜토리얼에 설정된 테이블에 따라 h1 호스트에서 h4로의 경로는 아래와 같다.
P4 튜토리얼 basic-tunnel의 이해
튜토리얼 코드 리뷰
/* -*- P4_16 -*- */
#include <core.p4>
#include <v1model.p4>
//새로운 사용자 설정 이더넷 타입 추가
const bit<16> TYPE_MYTUNNEL = 0x1212;
const bit<16> TYPE_IPV4 = 0x800;
/*************************************************************************
*********************** H E A D E R S ***********************************
*************************************************************************/
typedef bit<9> egressSpec_t;
typedef bit<48> macAddr_t;
typedef bit<32> ip4Addr_t;
header ethernet_t {
macAddr_t dstAddr;
macAddr_t srcAddr;
bit<16> etherType;
}
//터널링에 사용되는 헤더
header myTunnel_t {
bit<16> proto_id;
bit<16> dst_id;
}
header ipv4_t {
bit<4> version;
bit<4> ihl;
bit<8> diffserv;
bit<16> totalLen;
bit<16> identification;
bit<3> flags;
bit<13> fragOffset;
bit<8> ttl;
bit<8> protocol;
bit<16> hdrChecksum;
ip4Addr_t srcAddr;
ip4Addr_t dstAddr;
}
struct metadata {
/* empty */
}
//패킷의 헤더 구조체에 터널링 헤더 추가
struct headers {
ethernet_t ethernet;
myTunnel_t myTunnel;
ipv4_t ipv4;
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** P A R S E R ***********************************
*************************************************************************/
parser MyParser(packet_in packet,
out headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
state start {
transition parse_ethernet;
}
state parse_ethernet {
packet.extract(hdr.ethernet);
transition select(hdr.ethernet.etherType) {
//이더넷타입이 새로 만든 타입이라면 parse_myTunnel로 헤더 분리 이더넷타입에 따른 파서를 수행한다.
TYPE_MYTUNNEL: parse_myTunnel;
TYPE_IPV4: parse_ipv4;
default: accept;
}
}
state parse_myTunnel {
//터널링 헤더 분리
packet.extract(hdr.myTunnel);
//이후에 터널링 헤더 안의 proto_id가 ipv4라면 ipv4 헤더도 분리
transition select(hdr.myTunnel.proto_id) {
TYPE_IPV4: parse_ipv4;
default: accept;
}
}
state parse_ipv4 {
packet.extract(hdr.ipv4);
transition accept;
}
}
/*************************************************************************
************ C H E C K S U M V E R I F I C A T I O N *************
*************************************************************************/
control MyVerifyChecksum(inout headers hdr, inout metadata meta) {
apply { }
}
/*************************************************************************
************** I N G R E S S P R O C E S S I N G *******************
*************************************************************************/
control MyIngress(inout headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
action drop() {
mark_to_drop(standard_metadata);
}
action ipv4_forward(macAddr_t dstAddr, egressSpec_t port) {
standard_metadata.egress_spec = port;
hdr.ethernet.srcAddr = hdr.ethernet.dstAddr;
hdr.ethernet.dstAddr = dstAddr;
hdr.ipv4.ttl = hdr.ipv4.ttl - 1;
}
table ipv4_lpm {
key = {
hdr.ipv4.dstAddr: lpm;
}
actions = {
ipv4_forward;
drop;
NoAction;
}
size = 1024;
default_action = drop();
}
//터널링에 사용되는 action, 터널의 다음 목적지 포트를 인수로 받는다
action myTunnel_forward(egressSpec_t port) {
//나가는 포트를 설정
standard_metadata.egress_spec = port;
}
//새로운 테이블 설정
table myTunnel_exact {
key = {
//터널링 헤더의 dst_id를 key로 설정하고 구별 방법을 exact로 설정
hdr.myTunnel.dst_id: exact;
}
actions = {
//알맞는 action 설정
myTunnel_forward;
drop;
}
size = 1024;
default_action = drop();
}
apply {
//ipv4헤더가 유효하고 터널링 헤더가 유효하지 않다면 ipv4테이블로 포워딩을 진행한다.
if (hdr.ipv4.isValid() && !hdr.myTunnel.isValid()) {
// Process only non-tunneled IPv4 packets
ipv4_lpm.apply();
}
//터널링헤더가 유효하다면 터널링 테이블로 포워딩
if (hdr.myTunnel.isValid()) {
// process tunneled packets
myTunnel_exact.apply();
}
}
}
/*************************************************************************
**************** E G R E S S P R O C E S S I N G *******************
*************************************************************************/
control MyEgress(inout headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
apply { }
}
/*************************************************************************
************* C H E C K S U M C O M P U T A T I O N **************
*************************************************************************/
control MyComputeChecksum(inout headers hdr, inout metadata meta) {
apply {
update_checksum(
hdr.ipv4.isValid(),
{ hdr.ipv4.version,
hdr.ipv4.ihl,
hdr.ipv4.diffserv,
hdr.ipv4.totalLen,
hdr.ipv4.identification,
hdr.ipv4.flags,
hdr.ipv4.fragOffset,
hdr.ipv4.ttl,
hdr.ipv4.protocol,
hdr.ipv4.srcAddr,
hdr.ipv4.dstAddr },
hdr.ipv4.hdrChecksum,
HashAlgorithm.csum16);
}
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** D E P A R S E R *******************************
*************************************************************************/
control MyDeparser(packet_out packet, in headers hdr) {
apply {
packet.emit(hdr.ethernet);
//터널링 헤드도 같이 디파서 한다.
packet.emit(hdr.myTunnel);
packet.emit(hdr.ipv4);
}
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** S W I T C H *******************************
*************************************************************************/
V1Switch(
MyParser(),
MyVerifyChecksum(),
MyIngress(),
MyEgress(),
MyComputeChecksum(),
MyDeparser()
) main;
튜토리얼 실행결과
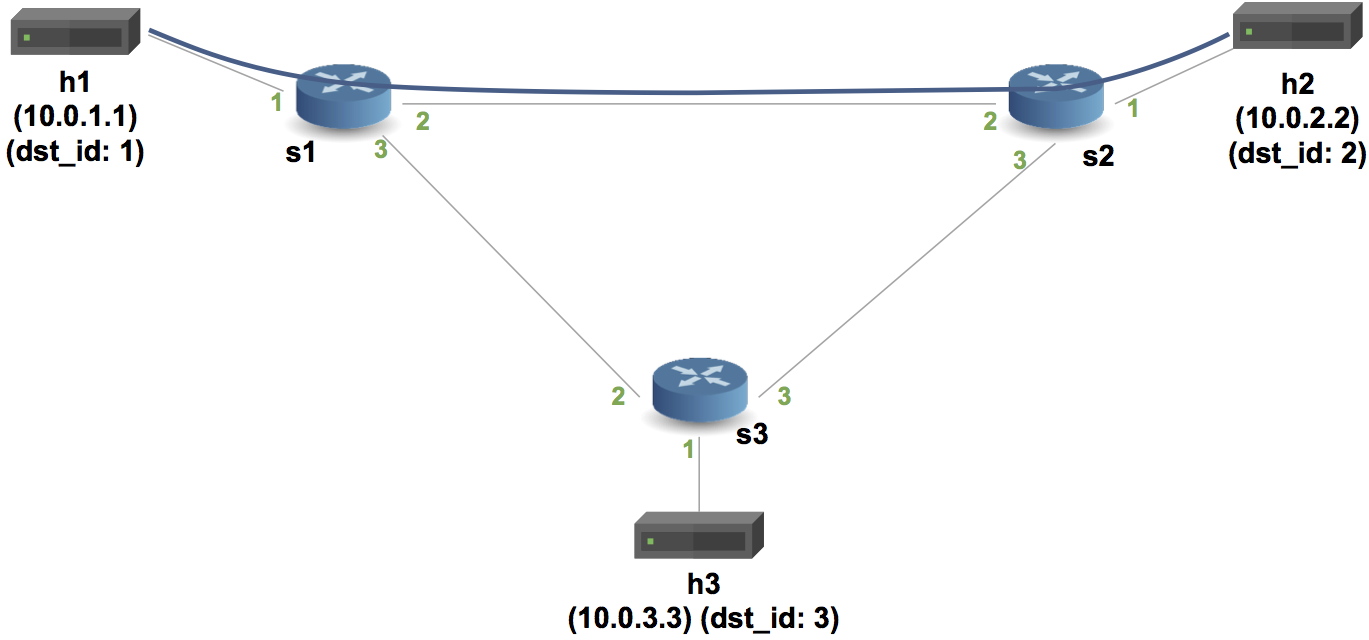
basic forwarding에서 이더넷헤더와 ipv4 헤더를 묶어서 보냈다면 basic tunnel에서는 이더넷헤더의 다음 부분 즉, ipv4를 터널링 헤더로 캡슐화 시켜서 ipv4의 목적지 ipAddr에 관계없이 연결된 통로(터널)로 이동하게 하는 구조이다.
예를 들어 위와 같은 토폴로지에서 h1 → h2 로 ping 을 보내낸다면 ipv4포워딩 테이블에 의해서 h1->s1->s2→h2로 이동한다
하지만 h1→h2로 ping을 s1의 2포트의 터널을 이용해서 보낸다면 ipv4의 헤더값에 관계없이 터널 헤더에 의해 h1->s1->s2→h2로 이동한다. 이말은 h1→h3으로 s1의 2포트의 터널을 이용해서 보낸다고 하더라도 ipv4헤더의 목적지인 h3(10.0.3.3)에 관계없이 h2에 도착하게 된다는 말이다.
P4 튜토리얼 P4runtime의 이해
P4runtime이란
공식문서에서 "P4 프로그램에서 정의한 장치의 데이터 평면 요소를 관리하기 위한 제어 평면 사양입니다."라고 정의하고 있다.
사전조건
이전 튜토리얼에서 sX-runtime.json파일을 사용해서 forwarding 테이블을 채워넣은 것과 다르게 runtime을 이용해서 동적으로 forwarding 테이블을 채워넣는 역할을 한다.
advanced_tunnel.p4 을 이용해서 p4프로그램을 실행한 후에 h1 ping -c1 h2 명령을 실행한 다음의 s1스위치의 로그내용이다.
[01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Processing packet received on port 1 [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser': start [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser' entering state 'start' [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Extracting header 'ethernet' [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Parser state 'start': key is 0800 [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Bytes parsed: 14 [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser' entering state 'parse_ipv4' [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Extracting header 'ipv4' [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Parser state 'parse_ipv4' has no switch, going to default next state [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Bytes parsed: 34 [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser': end [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'ingress': start [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(169) Condition "hdr.ipv4.isValid() && !hdr.myTunnel.isValid()" (node_2) is true [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Applying table 'MyIngress.ipv4_lpm' [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Looking up key: * hdr.ipv4.dstAddr : 0a000202 [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Table 'MyIngress.ipv4_lpm': miss //테이블이 채워지지 않았기 때문에 목적지인 h2의 ipAddr이랑 매치되는 내용이 없다 그래서 miss가 나고 noAction을 수행한다. [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Action entry is NoAction - [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Action NoAction [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(174) Condition "hdr.myTunnel.isValid()" (node_4) is false [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'ingress': end [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [50.0] [cxt 0] Egress port is 0 [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3034] [50.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'egress': start [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3034] [50.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'egress': end [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3034] [50.0] [cxt 0] Deparser 'deparser': start [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3034] [50.0] [cxt 0] Updating checksum 'cksum' [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3034] [50.0] [cxt 0] Deparsing header 'ethernet' [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3034] [50.0] [cxt 0] Deparsing header 'ipv4' [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3034] [50.0] [cxt 0] Deparser 'deparser': end [01:20:20.365] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3038] [50.0] [cxt 0] Transmitting packet of size 98 out of port 0
mycontroller.py을 이용해서 s1에 ingress rule과 egress rule을 추가한 후에 h1 ping -c1 h2 명령을 실행한 다음의 s1스위치의 로그내용이다.
[01:22:43.726] [bmv2] [W] [thread 3131] [P4Runtime] p4::tmp::P4DeviceConfig is deprecated [01:22:43.728] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3131] Set default default entry for table 'MyIngress.ipv4_lpm': NoAction - [01:22:43.728] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3131] Set default default entry for table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact': MyIngress.drop - [01:22:43.730] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3131] simple_switch target has been notified of a config swap [01:22:43.738] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3135] Entry 0 added to table 'MyIngress.ipv4_lpm' [01:22:43.738] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3135] Dumping entry 0 Match key: * hdr.ipv4.dstAddr : LPM 0a000202/32 Action entry: MyIngress.myTunnel_ingress - 64, [01:22:43.741] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3131] Entry 0 added to table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact' [01:22:43.741] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3131] Dumping entry 0 Match key: * hdr.myTunnel.dst_id : EXACT 00c8 Action entry: MyIngress.myTunnel_egress - 80000000111,1, /** s1에 ingress rule과 egress rule을 추가**/ [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Processing packet received on port 1 [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser': start [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser' entering state 'start' [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Extracting header 'ethernet' [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Parser state 'start': key is 0800 [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Bytes parsed: 14 [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser' entering state 'parse_ipv4' [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Extracting header 'ipv4' [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Parser state 'parse_ipv4' has no switch, going to default next state [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Bytes parsed: 34 [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser': end [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'ingress': start [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(169) Condition "hdr.ipv4.isValid() && !hdr.myTunnel.isValid()" (node_2) is true [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Applying table 'MyIngress.ipv4_lpm' [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Looking up key: * hdr.ipv4.dstAddr : 0a000202 [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Table 'MyIngress.ipv4_lpm': hit with handle 0 //테이블에 항목이 추가되어 h2의 ipAddr와 hit [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Dumping entry 0 Match key: * hdr.ipv4.dstAddr : LPM 0a000202/32 Action entry: MyIngress.myTunnel_ingress - 64, [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Action entry is MyIngress.myTunnel_ingress - 64, //hit한 항목의 action인 myTunnel_ingress를 실행한다. [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Action MyIngress.myTunnel_ingress [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(122) Primitive hdr.myTunnel.setValid() [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(123) Primitive hdr.myTunnel.dst_id = dst_id [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(124) Primitive hdr.myTunnel.proto_id = hdr.ethernet.etherType [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(5) Primitive 0x1212; ... [01:23:34.105] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(126) Primitive (bit<32>) hdr.myTunnel.dst_id [01:23:34.106] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(126) Primitive ingressTunnelCounter.count((bit<32>) hdr.myTunnel.dst_id) [01:23:34.106] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Updated counter 'MyIngress.ingressTunnelCounter' at index 100 [01:23:34.106] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(174) Condition "hdr.myTunnel.isValid()" (node_4) is true [01:23:34.106] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Applying table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact' [01:23:34.106] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Looking up key: * hdr.myTunnel.dst_id : 0064 [01:23:34.106] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact': miss //아직 tunnel의 전달 규칙 테이블이 추가되지 않았기 때문에 miss [01:23:34.106] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Action entry is MyIngress.drop - [01:23:34.106] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Action MyIngress.drop [01:23:34.106] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(111) Primitive mark_to_drop(standard_metadata) [01:23:34.106] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'ingress': end [01:23:34.106] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Egress port is 511 [01:23:34.106] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3033] [57.0] [cxt 0] Dropping packet at the end of ingress
아직 tunnel 테이블에 패킷 전달 규칙을 추가하지 않았기 때문에 s1에 패킷이 들어가기만 하고 전달되지 않은것을 확인할 수 있다.
튜토리얼 실행결과
이후에 제대로 된 mycontroller.py로 테이블을 채워 넣고 h1 ping -c1 h2를 실행했을 때
[02:02:54.048] [bmv2] [W] [thread 3663] [P4Runtime] p4::tmp::P4DeviceConfig is deprecated [02:02:54.050] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3663] Set default default entry for table 'MyIngress.ipv4_lpm': NoAction - [02:02:54.050] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3663] Set default default entry for table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact': MyIngress.drop - [02:02:54.052] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3663] simple_switch target has been notified of a config swap [02:02:54.059] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3667] Entry 0 added to table 'MyIngress.ipv4_lpm' [02:02:54.059] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3667] Dumping entry 0 Match key: * hdr.ipv4.dstAddr : LPM 0a000202/32 Action entry: MyIngress.myTunnel_ingress - 64, [02:02:54.060] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3663] Entry 0 added to table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact' // 패킷 전달 규칙까지 테이블에 추가 [02:02:54.060] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3663] Dumping entry 0 Match key: * hdr.myTunnel.dst_id : EXACT 0064 Action entry: MyIngress.myTunnel_forward - 2, [02:02:54.065] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3667] Entry 1 added to table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact' [02:02:54.065] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3667] Dumping entry 1 Match key: * hdr.myTunnel.dst_id : EXACT 00c8 Action entry: MyIngress.myTunnel_egress - 80000000111,1, [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Processing packet received on port 1 [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser': start [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser' entering state 'start' [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Extracting header 'ethernet' [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Parser state 'start': key is 0800 [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Bytes parsed: 14 [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser' entering state 'parse_ipv4' [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Extracting header 'ipv4' [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Parser state 'parse_ipv4' has no switch, going to default next state [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Bytes parsed: 34 [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser': end [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'ingress': start [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(169) Condition "hdr.ipv4.isValid() && !hdr.myTunnel.isValid()" (node_2) is true [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Applying table 'MyIngress.ipv4_lpm' [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Looking up key: * hdr.ipv4.dstAddr : 0a000202 [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Table 'MyIngress.ipv4_lpm': hit with handle 0 [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Dumping entry 0 Match key: * hdr.ipv4.dstAddr : LPM 0a000202/32 Action entry: MyIngress.myTunnel_ingress - 64, [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Action entry is MyIngress.myTunnel_ingress - 64, [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Action MyIngress.myTunnel_ingress [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(122) Primitive hdr.myTunnel.setValid() [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(123) Primitive hdr.myTunnel.dst_id = dst_id [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(124) Primitive hdr.myTunnel.proto_id = hdr.ethernet.etherType [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(5) Primitive 0x1212; ... [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(126) Primitive (bit<32>) hdr.myTunnel.dst_id [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(126) Primitive ingressTunnelCounter.count((bit<32>) hdr.myTunnel.dst_id) [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Updated counter 'MyIngress.ingressTunnelCounter' at index 100 [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(174) Condition "hdr.myTunnel.isValid()" (node_4) is true [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Applying table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact' [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Looking up key: * hdr.myTunnel.dst_id : 0064 [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact': hit with handle 0 // 터널을 통한 패킷 전송 규칙도 hit [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Dumping entry 0 Match key: * hdr.myTunnel.dst_id : EXACT 0064 Action entry: MyIngress.myTunnel_forward - 2, [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Action entry is MyIngress.myTunnel_forward - 2, [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Action MyIngress.myTunnel_forward [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(130) Primitive standard_metadata.egress_spec = port [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'ingress': end [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3602] [33.0] [cxt 0] Egress port is 2 [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3605] [33.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'egress': start [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3605] [33.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'egress': end [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3605] [33.0] [cxt 0] Deparser 'deparser': start [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3605] [33.0] [cxt 0] Updating checksum 'cksum' [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3605] [33.0] [cxt 0] Deparsing header 'ethernet' [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3605] [33.0] [cxt 0] Deparsing header 'myTunnel' [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3605] [33.0] [cxt 0] Deparsing header 'ipv4' [02:03:13.197] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3605] [33.0] [cxt 0] Deparser 'deparser': end [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3607] [33.0] [cxt 0] Transmitting packet of size 102 out of port 2 //정상적으로 s1의 port2로 패킷 전달
[02:02:54.054] [bmv2] [W] [thread 3666] [P4Runtime] p4::tmp::P4DeviceConfig is deprecated [02:02:54.056] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3666] Set default default entry for table 'MyIngress.ipv4_lpm': NoAction - [02:02:54.056] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3666] Set default default entry for table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact': MyIngress.drop - [02:02:54.057] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3666] simple_switch target has been notified of a config swap [02:02:54.062] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3672] Entry 0 added to table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact' [02:02:54.062] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3672] Dumping entry 0 Match key: * hdr.myTunnel.dst_id : EXACT 0064 Action entry: MyIngress.myTunnel_egress - 80000000222,1, [02:02:54.063] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3666] Entry 0 added to table 'MyIngress.ipv4_lpm' [02:02:54.063] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3666] Dumping entry 0 Match key: * hdr.ipv4.dstAddr : LPM 0a000101/32 Action entry: MyIngress.myTunnel_ingress - c8, [02:02:54.064] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3672] Entry 1 added to table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact' [02:02:54.064] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3672] Dumping entry 1 Match key: * hdr.myTunnel.dst_id : EXACT 00c8 Action entry: MyIngress.myTunnel_forward - 2, [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Processing packet received on port 2//s1에서 보낸 패킷을 s2의 port 2로 받았다. [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser': start [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser' entering state 'start' [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Extracting header 'ethernet' [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Parser state 'start': key is 1212 [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Bytes parsed: 14 [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser' entering state 'parse_myTunnel' [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Extracting header 'myTunnel' [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Parser state 'parse_myTunnel': key is 0800 [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Bytes parsed: 18 [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser' entering state 'parse_ipv4' [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Extracting header 'ipv4' [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Parser state 'parse_ipv4' has no switch, going to default next state [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Bytes parsed: 38 [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Parser 'parser': end [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'ingress': start [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(169) Condition "hdr.ipv4.isValid() && !hdr.myTunnel.isValid()" (node_2) is false [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(174) Condition "hdr.myTunnel.isValid()" (node_4) is true [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Applying table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact' [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Looking up key: * hdr.myTunnel.dst_id : 0064 [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Table 'MyIngress.myTunnel_exact': hit with handle 0 [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Dumping entry 0 Match key: * hdr.myTunnel.dst_id : EXACT 0064 Action entry: MyIngress.myTunnel_egress - 80000000222,1, [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Action entry is MyIngress.myTunnel_egress - 80000000222,1, [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Action MyIngress.myTunnel_egress [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(134) Primitive standard_metadata.egress_spec = port [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(135) Primitive hdr.ethernet.dstAddr = dstAddr [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(136) Primitive hdr.ethernet.etherType = hdr.myTunnel.proto_id [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(137) Primitive hdr.myTunnel.setInvalid() [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(138) Primitive (bit<32>) hdr.myTunnel.dst_id [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] advanced_tunnel.p4(138) Primitive egressTunnelCounter.count((bit<32>) hdr.myTunnel.dst_id) [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [T] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Updated counter 'MyIngress.egressTunnelCounter' at index 100 [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'ingress': end [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3620] [26.0] [cxt 0] Egress port is 1 [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3622] [26.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'egress': start [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3622] [26.0] [cxt 0] Pipeline 'egress': end [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3622] [26.0] [cxt 0] Deparser 'deparser': start [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3622] [26.0] [cxt 0] Updating checksum 'cksum' [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3622] [26.0] [cxt 0] Deparsing header 'ethernet' [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3622] [26.0] [cxt 0] Deparsing header 'ipv4' [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3622] [26.0] [cxt 0] Deparser 'deparser': end [02:03:13.198] [bmv2] [D] [thread 3625] [26.0] [cxt 0] Transmitting packet of size 98 out of port 1 //정상적으로 h2가 연결되어 있는 port 1로 패킷을 전달
튜토리얼 코드 리뷰
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import argparse
import os
import sys
from time import sleep
import grpc
# Import P4Runtime lib from parent utils dir
# Probably there's a better way of doing this.
sys.path.append(
os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)),
'../../utils/'))
import p4runtime_lib.bmv2
import p4runtime_lib.helper
from p4runtime_lib.switch import ShutdownAllSwitchConnections
SWITCH_TO_HOST_PORT = 1
SWITCH_TO_SWITCH_PORT = 2
def writeTunnelRules(p4info_helper, ingress_sw, egress_sw, tunnel_id,
dst_eth_addr, dst_ip_addr):
"""
Installs three rules:
1) An tunnel ingress rule on the ingress switch in the ipv4_lpm table that
encapsulates traffic into a tunnel with the specified ID
2) A transit rule on the ingress switch that forwards traffic based on
the specified ID
3) An tunnel egress rule on the egress switch that decapsulates traffic
with the specified ID and sends it to the host
:param p4info_helper: the P4Info helper
:param ingress_sw: the ingress switch connection
:param egress_sw: the egress switch connection
:param tunnel_id: the specified tunnel ID
:param dst_eth_addr: the destination Ethernet address to write in the
egress rule
:param dst_ip_addr: the destination IP to match in the ingress rule
"""
# 1) Tunnel Ingress Rule -> 패킷이 스위치에 들어올 때의 규칙을 ipv4 테이블에 설정한다. 즉, s1에 들어오는 각각의 패킷의 ipv4Addr에 맞는 action을 지정한다. 여기서는 패킷이 이동할 터널의 id를 myTunnel_ingress action에 전달한다.
table_entry = p4info_helper.buildTableEntry(
table_name="MyIngress.ipv4_lpm",
match_fields={
"hdr.ipv4.dstAddr": (dst_ip_addr, 32)
},
action_name="MyIngress.myTunnel_ingress",
action_params={
"dst_id": tunnel_id,
})
ingress_sw.WriteTableEntry(table_entry)
print("Installed ingress tunnel rule on %s" % ingress_sw.name)
# 2) Tunnel Transit Rule
# The rule will need to be added to the myTunnel_exact table and match on
# the tunnel ID (hdr.myTunnel.dst_id). Traffic will need to be forwarded
# using the myTunnel_forward action on the port connected to the next switch.
#
# For our simple topology, switch 1 and switch 2 are connected using a
# link attached to port 2 on both switches. We have defined a variable at
# the top of the file, SWITCH_TO_SWITCH_PORT, that you can use as the output
# port for this action.
#
# We will only need a transit rule on the ingress switch because we are
# using a simple topology. In general, you'll need on transit rule for
# each switch in the path (except the last switch, which has the egress rule),
# and you will need to select the port dynamically for each switch based on
# your topology.
# TODO build the transit rule
# TODO install the transit rule on the ingress switch
table_entry = p4info_helper.buildTableEntry( #tunnel 테이블에 규칙을 추가한다. 여기서는 tunnel헤더의 tunnel_id를 보고 패킷이 전송될 port를 지정해준다.
table_name="MyIngress.myTunnel_exact",
match_fields={
"hdr.myTunnel.dst_id": tunnel_id
},
action_name="MyIngress.myTunnel_forward",
action_params={
"port": SWITCH_TO_SWITCH_PORT
})
ingress_sw.WriteTableEntry(table_entry)
print("Installed transit tunnel rule on %s" % ingress_sw.name)
# 3) Tunnel Egress Rule
# For our simple topology, the host will always be located on the
# SWITCH_TO_HOST_PORT (port 1).
# In general, you will need to keep track of which port the host is
# connected to.
table_entry = p4info_helper.buildTableEntry( # tunnel을 모두 통과하고 호스트로 패킷을 전달할 때 tunnel 헤더의 tunnel_id에 따른 목적지 호스트의 ipAddr과 연결된 port를 지정해준다.
table_name="MyIngress.myTunnel_exact",
match_fields={
"hdr.myTunnel.dst_id": tunnel_id
},
action_name="MyIngress.myTunnel_egress",
action_params={
"dstAddr": dst_eth_addr,
"port": SWITCH_TO_HOST_PORT
})
egress_sw.WriteTableEntry(table_entry)
print("Installed egress tunnel rule on %s" % egress_sw.name)
def readTableRules(p4info_helper, sw):
"""
Reads the table entries from all tables on the switch.
:param p4info_helper: the P4Info helper
:param sw: the switch connection
"""
print('\n----- Reading tables rules for %s -----' % sw.name)
for response in sw.ReadTableEntries():
for entity in response.entities:
entry = entity.table_entry
# TODO For extra credit, you can use the p4info_helper to translate
# the IDs in the entry to names
table_name = p4info_helper.get_tables_name(entry.table_id)
print('%s: ' % table_name, end=' ')
for m in entry.match:
print(p4info_helper.get_match_field_name(table_name, m.field_id), end=' ')
print('%r' % (p4info_helper.get_match_field_value(m),), end=' ')
action = entry.action.action
action_name = p4info_helper.get_actions_name(action.action_id)
print('->', action_name, end=' ')
for p in action.params:
print(p4info_helper.get_action_param_name(action_name, p.param_id), end=' ')
print('%r' % p.value, end=' ')
print()
def printCounter(p4info_helper, sw, counter_name, index):
"""
Reads the specified counter at the specified index from the switch. In our
program, the index is the tunnel ID. If the index is 0, it will return all
values from the counter.
:param p4info_helper: the P4Info helper
:param sw: the switch connection
:param counter_name: the name of the counter from the P4 program
:param index: the counter index (in our case, the tunnel ID)
"""
for response in sw.ReadCounters(p4info_helper.get_counters_id(counter_name), index):
for entity in response.entities:
counter = entity.counter_entry
print("%s %s %d: %d packets (%d bytes)" % (
sw.name, counter_name, index,
counter.data.packet_count, counter.data.byte_count
))
def printGrpcError(e):
print("gRPC Error:", e.details(), end=' ')
status_code = e.code()
print("(%s)" % status_code.name, end=' ')
traceback = sys.exc_info()[2]
print("[%s:%d]" % (traceback.tb_frame.f_code.co_filename, traceback.tb_lineno))
def main(p4info_file_path, bmv2_file_path):
# Instantiate a P4Runtime helper from the p4info file
p4info_helper = p4runtime_lib.helper.P4InfoHelper(p4info_file_path)
try:
# Create a switch connection object for s1 and s2;
# this is backed by a P4Runtime gRPC connection.
# Also, dump all P4Runtime messages sent to switch to given txt files.
s1 = p4runtime_lib.bmv2.Bmv2SwitchConnection(
name='s1',
address='127.0.0.1:50051',
device_id=0,
proto_dump_file='logs/s1-p4runtime-requests.txt')
s2 = p4runtime_lib.bmv2.Bmv2SwitchConnection(
name='s2',
address='127.0.0.1:50052',
device_id=1,
proto_dump_file='logs/s2-p4runtime-requests.txt')
# Send master arbitration update message to establish this controller as
# master (required by P4Runtime before performing any other write operation)
s1.MasterArbitrationUpdate()
s2.MasterArbitrationUpdate()
# Install the P4 program on the switches
s1.SetForwardingPipelineConfig(p4info=p4info_helper.p4info,
bmv2_json_file_path=bmv2_file_path)
print("Installed P4 Program using SetForwardingPipelineConfig on s1")
s2.SetForwardingPipelineConfig(p4info=p4info_helper.p4info,
bmv2_json_file_path=bmv2_file_path)
print("Installed P4 Program using SetForwardingPipelineConfig on s2")
# Write the rules that tunnel traffic from h1 to h2
writeTunnelRules(p4info_helper, ingress_sw=s1, egress_sw=s2, tunnel_id=100,
dst_eth_addr="08:00:00:00:02:22", dst_ip_addr="10.0.2.2")
# Write the rules that tunnel traffic from h2 to h1
writeTunnelRules(p4info_helper, ingress_sw=s2, egress_sw=s1, tunnel_id=200,
dst_eth_addr="08:00:00:00:01:11", dst_ip_addr="10.0.1.1")
# TODO Uncomment the following two lines to read table entries from s1 and s2
readTableRules(p4info_helper, s1)
readTableRules(p4info_helper, s2)
# Print the tunnel counters every 2 seconds
while True:
sleep(2)
print('\n----- Reading tunnel counters -----')
printCounter(p4info_helper, s1, "MyIngress.ingressTunnelCounter", 100)
printCounter(p4info_helper, s2, "MyIngress.egressTunnelCounter", 100)
printCounter(p4info_helper, s2, "MyIngress.ingressTunnelCounter", 200)
printCounter(p4info_helper, s1, "MyIngress.egressTunnelCounter", 200)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print(" Shutting down.")
except grpc.RpcError as e:
printGrpcError(e)
ShutdownAllSwitchConnections()
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='P4Runtime Controller')
parser.add_argument('--p4info', help='p4info proto in text format from p4c',
type=str, action="store", required=False,
default='./build/advanced_tunnel.p4.p4info.txt')
parser.add_argument('--bmv2-json', help='BMv2 JSON file from p4c',
type=str, action="store", required=False,
default='./build/advanced_tunnel.json')
args = parser.parse_args()
if not os.path.exists(args.p4info):
parser.print_help()
print("\np4info file not found: %s\nHave you run 'make'?" % args.p4info)
parser.exit(1)
if not os.path.exists(args.bmv2_json):
parser.print_help()
print("\nBMv2 JSON file not found: %s\nHave you run 'make'?" % args.bmv2_json)
parser.exit(1)
main(args.p4info, args.bmv2_json)
P4 튜토리얼 mri의 이해
mri란
mri란 multi-hop route inspection의 약자로 패킷에 패킷이 지나온 경로를 추가함으로써 패킷의 이동경로와 같은 부가정보를 알 수 있게 하는 in-Band Network Telemetry(INT)의 축소버전이다.
MRI를 통해 사용자는 모든 패킷이 통과하는 대기열의 경로와 길이를 추적할 수 있습니다.
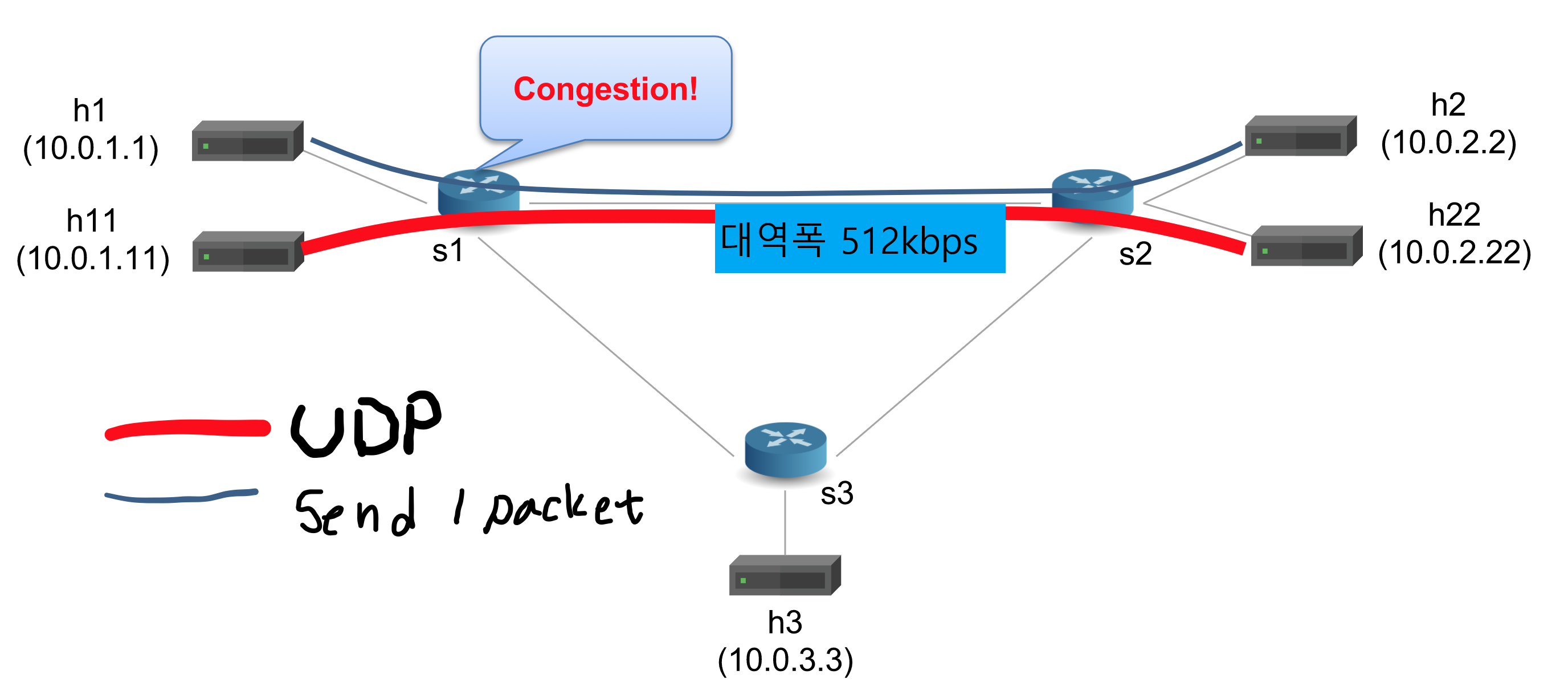
튜토리얼 사전 조건
s1과 s2의 링크의 대역폭은 512kbps로 제한되어 있다. 이상태에서 s1과 s2의 통로를 h11↔h22가 UDP 통신을 하고 h1↔h2가 패킷을 주고 받는 조건이다.
대역폭이 512kbps인 링크를 UDP통신으로 많이 소모하고 있기 때문에 h1↔2h의 패킷교환은 느리게 이루어질 수 밖에 없는데 이때의 h1과 h2가 주고받는 패킷에 스위치를 지날때 마다 mri를 추가하여 경로와 해당 경로를 지날 때의 패킷 대기열 등을 확인해보는 것이 튜토리얼의 목적이다.
튜토리얼 코드 리뷰
/* -*- P4_16 -*- */
#include <core.p4>
#include <v1model.p4>
const bit<8> UDP_PROTOCOL = 0x11;
const bit<16> TYPE_IPV4 = 0x800;
const bit<5> IPV4_OPTION_MRI = 31;
#define MAX_HOPS 9
/*************************************************************************
*********************** H E A D E R S ***********************************
*************************************************************************/
typedef bit<9> egressSpec_t;
typedef bit<48> macAddr_t;
typedef bit<32> ip4Addr_t;
typedef bit<32> switchID_t;
typedef bit<32> qdepth_t;
header ethernet_t {
macAddr_t dstAddr;
macAddr_t srcAddr;
bit<16> etherType;
}
header ipv4_t {
bit<4> version;
bit<4> ihl;
bit<8> diffserv;
bit<16> totalLen;
bit<16> identification;
bit<3> flags;
bit<13> fragOffset;
bit<8> ttl;
bit<8> protocol;
bit<16> hdrChecksum;
ip4Addr_t srcAddr;
ip4Addr_t dstAddr;
}
//ipv4 헤더에 옵션을 추가한다. 이는 이 패킷에 mri를 추가하겠다는 의미를 내포할 수 있게된다.
header ipv4_option_t {
bit<1> copyFlag;
bit<2> optClass;
bit<5> option;
bit<8> optionLength;
}
//mri 개수를 저장한다.
header mri_t {
bit<16> count;
}
//지나온 스위치의 id와 해당 스위치에서 패킷이 빠져나올때 남아있는 대기열의 깊이를 저장한다.
header switch_t {
switchID_t swid;//지나온 스위치의 id
qdepth_t qdepth;//스위치에서 패킷이 빠져나올때 남아있는 대기열의 깊이
}
struct ingress_metadata_t {
bit<16> count;
}
struct parser_metadata_t {
bit<16> remaining;
}
//추가적인 메타데이터 구조체
struct metadata {
ingress_metadata_t ingress_metadata;
parser_metadata_t parser_metadata;
}
//완성된 패킷의 전체 헤더
struct headers {
ethernet_t ethernet;
ipv4_t ipv4;
ipv4_option_t ipv4_option;//mri는 ipv4의 option으로 저장된다. 즉 ipv4헤더에 포함된다.
mri_t mri;
switch_t[MAX_HOPS] swtraces;//최대 MAX_HOPS개의 경로를 저장할 수 있다.
}
error { IPHeaderTooShort }
/*************************************************************************
*********************** P A R S E R ***********************************
*************************************************************************/
parser MyParser(packet_in packet,
out headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
state start {
transition parse_ethernet;
}
state parse_ethernet {
packet.extract(hdr.ethernet);
transition select(hdr.ethernet.etherType) {
TYPE_IPV4: parse_ipv4;
default: accept;
}
}
state parse_ipv4 {
packet.extract(hdr.ipv4);
verify(hdr.ipv4.ihl >= 5, error.IPHeaderTooShort);
transition select(hdr.ipv4.ihl) {
5 : accept;
default : parse_ipv4_option;
}
}
state parse_ipv4_option {
packet.extract(hdr.ipv4_option);
transition select(hdr.ipv4_option.option) {
IPV4_OPTION_MRI: parse_mri;
default: accept;
}
}
state parse_mri {
packet.extract(hdr.mri);
//헤더의 mri의 개수를 읽어온다.
meta.parser_metadata.remaining = hdr.mri.count;
transition select(meta.parser_metadata.remaining) {//mri가 1개라도 있다면 mri를 추출하기 위해 parse_swtrace 상태로 전이한다.
0 : accept;
default: parse_swtrace;
}
}
state parse_swtrace {
packet.extract(hdr.swtraces.next);//경로를 추출한다.
meta.parser_metadata.remaining = meta.parser_metadata.remaining - 1;//추출할 mri의 개수를 1씩 줄인다.
transition select(meta.parser_metadata.remaining) {//추출할 mri가 남아있다면 재귀적으로 계속 추출한다.
0 : accept;
default: parse_swtrace;
}
}
}
/*************************************************************************
************ C H E C K S U M V E R I F I C A T I O N *************
*************************************************************************/
control MyVerifyChecksum(inout headers hdr, inout metadata meta) {
apply { }
}
/*************************************************************************
************** I N G R E S S P R O C E S S I N G *******************
*************************************************************************/
control MyIngress(inout headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
action drop() {
mark_to_drop(standard_metadata);
}
action ipv4_forward(macAddr_t dstAddr, egressSpec_t port) {
standard_metadata.egress_spec = port;
hdr.ethernet.srcAddr = hdr.ethernet.dstAddr;
hdr.ethernet.dstAddr = dstAddr;
hdr.ipv4.ttl = hdr.ipv4.ttl - 1;
}
table ipv4_lpm {
key = {
hdr.ipv4.dstAddr: lpm;
}
actions = {
ipv4_forward;
drop;
NoAction;
}
size = 1024;
default_action = NoAction();
}
apply {
if (hdr.ipv4.isValid()) {
ipv4_lpm.apply();
}
}
}
/*************************************************************************
**************** E G R E S S P R O C E S S I N G *******************
*************************************************************************/
control MyEgress(inout headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
//스위치에서 패킷이 나갈때 mri를 추가한다.
action add_swtrace(switchID_t swid) {
hdr.mri.count = hdr.mri.count + 1;//mri 개수 증가
hdr.swtraces.push_front(1);//맨앞에 mri추가
// According to the P4_16 spec, pushed elements are invalid, so we need
// to call setValid(). Older bmv2 versions would mark the new header(s)
// valid automatically (P4_14 behavior), but starting with version 1.11,
// bmv2 conforms with the P4_16 spec.
hdr.swtraces[0].setValid();
hdr.swtraces[0].swid = swid;//추가한 mri에 스위치 id 설정
hdr.swtraces[0].qdepth = (qdepth_t)standard_metadata.deq_qdepth;//추가한 mri에 대기열의 남아있는 깊이를 설정
hdr.ipv4.ihl = hdr.ipv4.ihl + 2;//ipv4헤더가 총 8byte 증가 했기 때문에 ihl값을 2만큼 증가시킨다.
hdr.ipv4_option.optionLength = hdr.ipv4_option.optionLength + 8;//ipv4 옵션이 총 8byte 증가 했기 때문에 8만큼 증가시킨다.
hdr.ipv4.totalLen = hdr.ipv4.totalLen + 8;//ipv4 헤더 + 데이터가 총 8byte 증가 했기 때문에 8만큼 증가시킨다.
}
table swtrace {
actions = {
add_swtrace;
NoAction;
}
default_action = NoAction();
}
apply {
if (hdr.mri.isValid()) {//mri가 유효하다면 실행한다.
swtrace.apply();
}
}
}
/*************************************************************************
************* C H E C K S U M C O M P U T A T I O N **************
*************************************************************************/
control MyComputeChecksum(inout headers hdr, inout metadata meta) {
apply {
update_checksum(
hdr.ipv4.isValid(),
{ hdr.ipv4.version,
hdr.ipv4.ihl,
hdr.ipv4.diffserv,
hdr.ipv4.totalLen,
hdr.ipv4.identification,
hdr.ipv4.flags,
hdr.ipv4.fragOffset,
hdr.ipv4.ttl,
hdr.ipv4.protocol,
hdr.ipv4.srcAddr,
hdr.ipv4.dstAddr },
hdr.ipv4.hdrChecksum,
HashAlgorithm.csum16);
}
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** D E P A R S E R *******************************
*************************************************************************/
control MyDeparser(packet_out packet, in headers hdr) {
apply {
packet.emit(hdr.ethernet);
packet.emit(hdr.ipv4);
packet.emit(hdr.ipv4_option);
packet.emit(hdr.mri);
packet.emit(hdr.swtraces);
}
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** S W I T C H *******************************
*************************************************************************/
V1Switch(
MyParser(),
MyVerifyChecksum(),
MyIngress(),
MyEgress(),
MyComputeChecksum(),
MyDeparser()
) main;
튜토리얼 실행 결과
h1→h2로 패킷을 보내고 h2에서 받은 패킷을 분석한 결과이다. ip헤더의 옵션을 보면 mri가 존재하고 mri안에 지나온 스위치의 id와 스위치의 대기열이 저장되어 있는 것을 볼 수 있다.
위 결과는 h1→h2로 패킷을 보냈고 h1->s1->s2→h2의 경로로 패킷이 이동했으며 s1스위치에서 패킷이 나올때 대기열에 남은 패킷들이 17개이고 s2를 나올때는 남은 패킷이 없었다는 것을 알 수 있다.
이처럼 mri를 통해 패킷이 지나온 경로에 대한 정보를 알 수 있고 더 확장된 개념인 INT를 통해 패킷이 지나온 경로에 대한 다양한 정보를 얻고 네트워크 경로 상의 어느 부분이 장애가 있다던가 속도가 느리다던가를 분석할 수 있다는 것을 알 수 있었다.
P4 튜토리얼 sourceroute의 이해
사전 조건
소스 라우팅
ㅇ 패킷을 보내기 전에,
- 송신측에서 수신측까지 가는 모든 경로를 리스트로 만들어두어,
- 이를 패킷의 헤더에 넣어 보내는 방식
스위치에서 포워딩 테이블을 이용해서 패킷을 전달해주는것이 아닌 패킷자체에 어떤 스위치를 거쳐갈것인지를 넣어서 패킷을 전달한다.
튜토리얼 코드 리뷰
/* -*- P4_16 -*- */
#include <core.p4>
#include <v1model.p4>
const bit<16> TYPE_IPV4 = 0x800;
const bit<16> TYPE_SRCROUTING = 0x1234;
#define MAX_HOPS 9
/*************************************************************************
*********************** H E A D E R S ***********************************
*************************************************************************/
typedef bit<9> egressSpec_t;
typedef bit<48> macAddr_t;
typedef bit<32> ip4Addr_t;
header ethernet_t {
macAddr_t dstAddr;
macAddr_t srcAddr;
bit<16> etherType;
}
//패킷의 이동 경로를 저장할 헤더이다.
header srcRoute_t {
bit<1> bos;
bit<15> port;
}
header ipv4_t {
bit<4> version;
bit<4> ihl;
bit<8> diffserv;
bit<16> totalLen;
bit<16> identification;
bit<3> flags;
bit<13> fragOffset;
bit<8> ttl;
bit<8> protocol;
bit<16> hdrChecksum;
ip4Addr_t srcAddr;
ip4Addr_t dstAddr;
}
struct metadata {
/* empty */
}
//패킷 헤더에 패킷 경로 헤더를 추가
struct headers {
ethernet_t ethernet;
srcRoute_t[MAX_HOPS] srcRoutes;
ipv4_t ipv4;
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** P A R S E R ***********************************
*************************************************************************/
parser MyParser(packet_in packet,
out headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
state start {
transition parse_ethernet;
}
state parse_ethernet {
packet.extract(hdr.ethernet);
transition select(hdr.ethernet.etherType) {
TYPE_SRCROUTING: parse_srcRouting;
default: accept;
}
}
//소스라우팅 헤더가 있다면 bos(스택의 바닥)까지 경로를 추출한다.
state parse_srcRouting {
packet.extract(hdr.srcRoutes.next);
transition select(hdr.srcRoutes.last.bos) {
1: parse_ipv4;
default: parse_srcRouting;
}
}
state parse_ipv4 {
packet.extract(hdr.ipv4);
transition accept;
}
}
/*************************************************************************
************ C H E C K S U M V E R I F I C A T I O N *************
*************************************************************************/
control MyVerifyChecksum(inout headers hdr, inout metadata meta) {
apply { }
}
/*************************************************************************
************** I N G R E S S P R O C E S S I N G *******************
*************************************************************************/
control MyIngress(inout headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
action drop() {
mark_to_drop(standard_metadata);
}
//소스라우팅 헤더의 스택에서 경로 하나를 pop한다.
action srcRoute_nhop() {
standard_metadata.egress_spec = (bit<9>)hdr.srcRoutes[0].port;
hdr.srcRoutes.pop_front(1);
}
//패킷에 지정한 모든 경로를 다 돌았다면 패킷 헤더(이더넷 헤더타입)을 ipv4로 바꾼다.
action srcRoute_finish() {
hdr.ethernet.etherType = TYPE_IPV4;
}
action update_ttl(){
hdr.ipv4.ttl = hdr.ipv4.ttl - 1;
}
apply {
if (hdr.srcRoutes[0].isValid()){
if (hdr.srcRoutes[0].bos == 1){//이번 경로가 마지막이라면 패킷을 ipv4로 바꾼다.
srcRoute_finish();
}
srcRoute_nhop();//경로를 pop
if (hdr.ipv4.isValid()){
update_ttl();
}
}else{
drop();
}
}
}
/*************************************************************************
**************** E G R E S S P R O C E S S I N G *******************
*************************************************************************/
control MyEgress(inout headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
apply { }
}
/*************************************************************************
************* C H E C K S U M C O M P U T A T I O N **************
*************************************************************************/
control MyComputeChecksum(inout headers hdr, inout metadata meta) {
apply { }
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** D E P A R S E R *******************************
*************************************************************************/
control MyDeparser(packet_out packet, in headers hdr) {
apply {
packet.emit(hdr.ethernet);
packet.emit(hdr.srcRoutes);
packet.emit(hdr.ipv4);
}
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** S W I T C H *******************************
*************************************************************************/
V1Switch(
MyParser(),
MyVerifyChecksum(),
MyIngress(),
MyEgress(),
MyComputeChecksum(),
MyDeparser()
) main;
튜토리얼 실행결과
토폴로지의 모든 스위치를 모두 돌아서 h1→h2로 패킷전송이 성공했다.
P4 튜토리얼 Load balancing의 이해
사전 조건
간단한 버전의 Equal-Cost Multipath Forwarding을 기반으로 한 형태의 로드 밸런싱을 구현합니다. 구현할 스위치는 두 개의 테이블을 사용하여 임의로 두 개의 대상 호스트 중 하나로 패킷을 전달합니다. 첫 번째 테이블은 해시 함수(소스 및 대상 IP 주소, IP 프로토콜, 소스 및 대상 TCP 포트로 구성된 5-튜플에 적용됨)를 사용하여 두 호스트 중 하나를 선택합니다. 두 번째 테이블은 계산된 해시 값을 사용하여 선택한 호스트로 패킷을 전달합니다.
튜토리얼 코드 리뷰
/* -*- P4_16 -*- */
#include <core.p4>
#include <v1model.p4>
/*************************************************************************
*********************** H E A D E R S ***********************************
*************************************************************************/
header ethernet_t {
bit<48> dstAddr;
bit<48> srcAddr;
bit<16> etherType;
}
header ipv4_t {
bit<4> version;
bit<4> ihl;
bit<8> diffserv;
bit<16> totalLen;
bit<16> identification;
bit<3> flags;
bit<13> fragOffset;
bit<8> ttl;
bit<8> protocol;
bit<16> hdrChecksum;
bit<32> srcAddr;
bit<32> dstAddr;
}
//tcp 헤더
header tcp_t {
bit<16> srcPort;
bit<16> dstPort;
bit<32> seqNo;
bit<32> ackNo;
bit<4> dataOffset;
bit<3> res;
bit<3> ecn;
bit<6> ctrl;
bit<16> window;
bit<16> checksum;
bit<16> urgentPtr;
}
//ecmp 선택자
struct metadata {
bit<14> ecmp_select;
}
struct headers {
ethernet_t ethernet;
ipv4_t ipv4;
tcp_t tcp;
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** P A R S E R ***********************************
*************************************************************************/
parser MyParser(packet_in packet,
out headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
state start {
transition parse_ethernet;
}
state parse_ethernet {
packet.extract(hdr.ethernet);
transition select(hdr.ethernet.etherType) {
0x800: parse_ipv4;
default: accept;
}
}
state parse_ipv4 {
packet.extract(hdr.ipv4);
transition select(hdr.ipv4.protocol) {
6: parse_tcp;
default: accept;
}
}
state parse_tcp {
packet.extract(hdr.tcp);
transition accept;
}
}
/*************************************************************************
************ C H E C K S U M V E R I F I C A T I O N *************
*************************************************************************/
control MyVerifyChecksum(inout headers hdr, inout metadata meta) {
apply { }
}
/*************************************************************************
************** I N G R E S S P R O C E S S I N G *******************
*************************************************************************/
control MyIngress(inout headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
action drop() {
mark_to_drop(standard_metadata);
}
action set_ecmp_select(bit<16> ecmp_base, bit<32> ecmp_count) {
//소스 및 대상 IP 주소, IP 프로토콜, 소스 및 대상 TCP 포트로 해쉬값을 얻고 ecmp_select에 저장한다.
hash(meta.ecmp_select,
HashAlgorithm.crc16,
ecmp_base,
{ hdr.ipv4.srcAddr,
hdr.ipv4.dstAddr,
hdr.ipv4.protocol,
hdr.tcp.srcPort,
hdr.tcp.dstPort },
ecmp_count);
}
action set_nhop(bit<48> nhop_dmac, bit<32> nhop_ipv4, bit<9> port) {//나갈 포드를 지정한다.
hdr.ethernet.dstAddr = nhop_dmac;
hdr.ipv4.dstAddr = nhop_ipv4;
standard_metadata.egress_spec = port;
hdr.ipv4.ttl = hdr.ipv4.ttl - 1;
}
table ecmp_group {//어떤 ecmp 그룹인지를 판별한다.
key = {
hdr.ipv4.dstAddr: lpm;
}
actions = {
drop;
set_ecmp_select;
}
size = 1024;
}
table ecmp_nhop {//ecmp그룹에 맞는 목적지, 경로를 지정한다.
key = {
meta.ecmp_select: exact;
}
actions = {
drop;
set_nhop;
}
size = 2;
}
apply {
if (hdr.ipv4.isValid() && hdr.ipv4.ttl > 0) {
ecmp_group.apply();
ecmp_nhop.apply();
}
}
}
/*************************************************************************
**************** E G R E S S P R O C E S S I N G *******************
*************************************************************************/
control MyEgress(inout headers hdr,
inout metadata meta,
inout standard_metadata_t standard_metadata) {
//이더넷의 srcAddr을 수정한다.
action rewrite_mac(bit<48> smac) {
hdr.ethernet.srcAddr = smac;
}
action drop() {
mark_to_drop(standard_metadata);
}
table send_frame {//나가는 포트에 맞게 이더넷 헤더 수정
key = {
standard_metadata.egress_port: exact;
}
actions = {
rewrite_mac;
drop;
}
size = 256;
}
apply {
send_frame.apply();
}
}
/*************************************************************************
************* C H E C K S U M C O M P U T A T I O N **************
*************************************************************************/
control MyComputeChecksum(inout headers hdr, inout metadata meta) {
apply {
update_checksum(
hdr.ipv4.isValid(),
{ hdr.ipv4.version,
hdr.ipv4.ihl,
hdr.ipv4.diffserv,
hdr.ipv4.totalLen,
hdr.ipv4.identification,
hdr.ipv4.flags,
hdr.ipv4.fragOffset,
hdr.ipv4.ttl,
hdr.ipv4.protocol,
hdr.ipv4.srcAddr,
hdr.ipv4.dstAddr },
hdr.ipv4.hdrChecksum,
HashAlgorithm.csum16);
}
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** D E P A R S E R *******************************
*************************************************************************/
control MyDeparser(packet_out packet, in headers hdr) {
apply {
packet.emit(hdr.ethernet);
packet.emit(hdr.ipv4);
packet.emit(hdr.tcp);
}
}
/*************************************************************************
*********************** S W I T C H *******************************
*************************************************************************/
V1Switch(
MyParser(),
MyVerifyChecksum(),
MyIngress(),
MyEgress(),
MyComputeChecksum(),
MyDeparser()
) main;
튜토리얼 실행결과
h1에서 자기 자신에게 보낼 패킷을 보내면 패킷의 TCP 헤더에 따라 목적지 호스트가 바뀌는 것을 볼 수 있다.